In most cases, foot surgery is often chosen as the last available option for conditions that have otherwise been unsuccessfully treated. Surgery may be necessary for several reasons, including the removal of foot deformities (e.g. bone spurs or bunions), arthritis problems, reconstruction due to injury, and congenital malformations (e.g. club foot or flat feet). Regardless of one’s age, foot surgery may be the only successful option for treatment for certain conditions.
The type of surgery one undergoes depends on the type of foot condition the patient has. For the removal of a bunion growth, a bunionectomy is necessary. If the bones in the feet need to be realigned or fused together, a surgical fusion of the foot is needed. For pain or nerve issues, a patient may require surgery in which the tissues surrounding the painful nerve are removed. Initially, less invasive treatments are generally attempted; surgery is often the last measure taken if other treatments are unsuccessful.
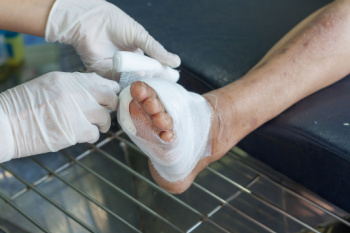
While in many cases surgery is often deemed as the final resort, choosing surgery comes with certain benefits. The associated pain experienced in relation to the particular condition is often relieved with surgery, allowing patients to quickly resume daily activities. The greatest benefit, however, is that surgery generally eliminates the problem immediately.
Podiatry history has shown that foot treatments continue to evolve over time. In the field of foot surgery, endoscopic surgery is just one of the many advanced forms of surgery. As technology vastly improves so too will the various techniques in foot surgery, which already require smaller and smaller incisions with the use of better and more efficient tools. Thanks to such innovations, surgery is no longer as invasive as it was in the past, allowing for faster and easier recoveries.